
At My CPA Advisory and Accounting Partners, we often field questions about the tax efficiency of popular investment options. One common query is the VTI vs VTSAX tax efficiency comparison.
These two Vanguard funds, while similar in many ways, have distinct characteristics that can impact their tax implications. Understanding these differences is key for investors looking to optimize their portfolios and minimize their tax burden.
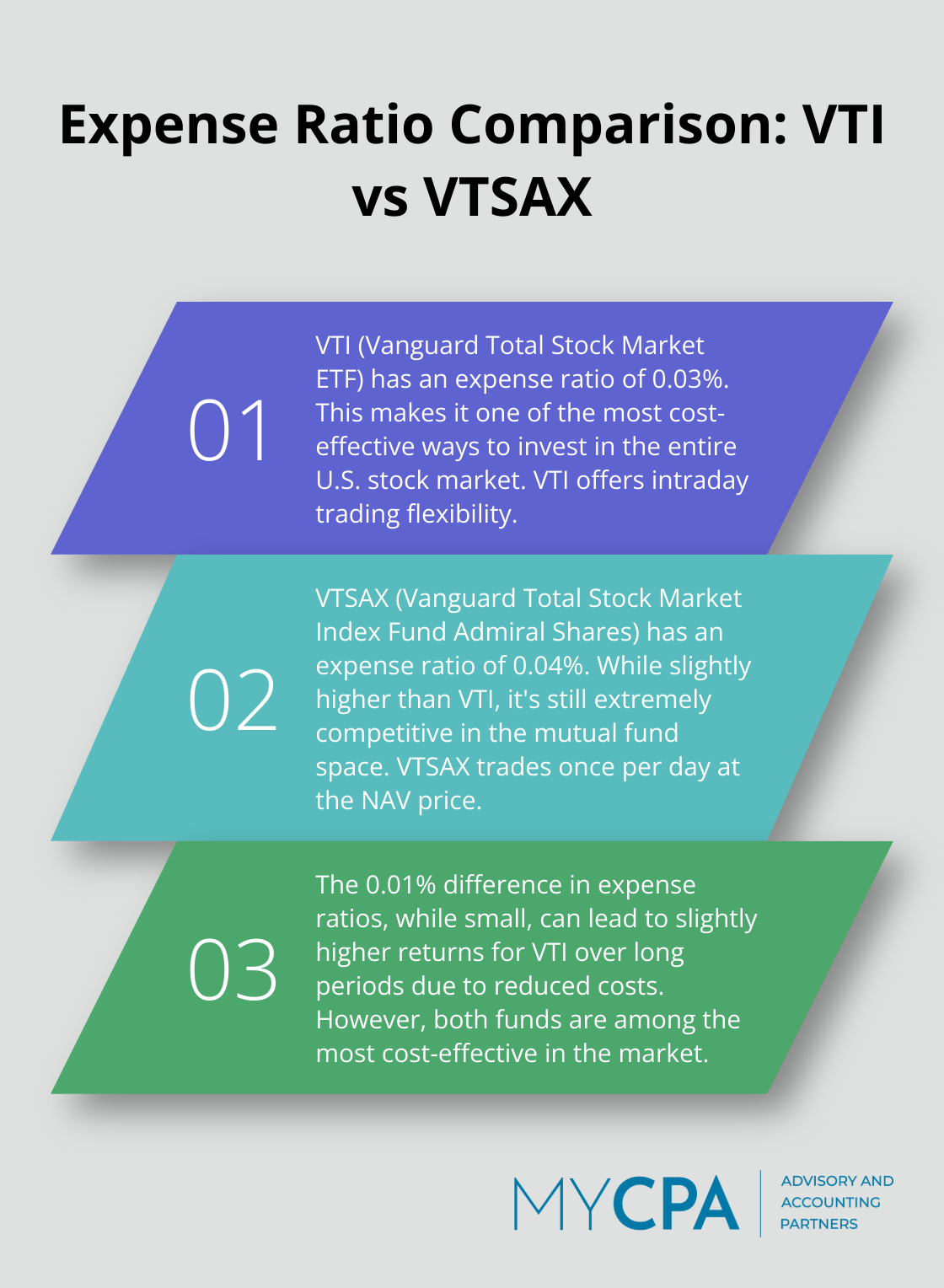
VTI (Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF) tracks the CRSP US Total Market Index. This index represents approximately 100% of the investable U.S. stock market, offering broad exposure to large-, mid-, and small-cap stocks. VTI has an expense ratio of 0.03%, making it one of the most cost-effective ways to invest in the entire U.S. stock market.
VTI’s trading flexibility stands out as a key advantage. Investors can buy and sell shares throughout the trading day at market prices. This feature benefits those who want to execute trades at specific times or capitalize on intraday price movements.
VTSAX (Vanguard Total Stock Market Index Fund Admiral Shares) is the mutual fund version of VTI, also tracking the CRSP US Total Market Index. It offers the same broad market exposure but with a slightly different structure. As of April 30, 2023, VTSAX has an expense ratio of 0.04%, marginally higher than VTI but still extremely competitive in the mutual fund space.
Unlike VTI, VTSAX trades only once per day at the net asset value (NAV) price calculated at market close. This feature simplifies the investment process for those who prefer a set-it-and-forget-it approach.
While both funds offer similar market exposure, their structural differences impact how they fit into an investor’s strategy. VTI’s lower expense ratio (0.03% vs 0.04%) might seem negligible, but over long periods, it can lead to slightly higher returns due to reduced costs.
VTSAX requires a minimum investment of $3,000, which might present a barrier for some investors. In contrast, VTI can be purchased for the price of a single share (approximately $200 as of May 16, 2025 – note: this price is hypothetical and for illustration purposes only).
For those focused on tax efficiency, VTI’s ETF structure traditionally offers advantages in managing capital gains distributions. However, Vanguard’s unique patented structure for VTSAX has narrowed this gap significantly.
The choice between VTI and VTSAX often depends on individual investment goals, tax situations, and personal preferences. VTI offers more flexibility and potentially lower costs, while VTSAX can advantage those who prefer automatic investments or dollar-cost averaging strategies.
Investors should consider their specific needs and consult with financial professionals to determine which option aligns best with their overall investment strategy. The next section will explore the tax efficiency aspects of these two funds in greater detail, providing insights into how they might impact an investor’s tax situation.
VTI, as an ETF, holds an advantage in managing capital gains distributions. Its structure permits in-kind redemptions, which minimizes taxable events. Because index mutual funds and ETFs generally trade less frequently, they tend to be more tax-efficient and have lower expense ratios than actively managed funds.
VTSAX, though a mutual fund, has kept capital gains distributions low. Vanguard’s previously patented ETF-as-a-share class fund structure has significantly reduced the gap with ETFs. VTSAX hasn’t distributed capital gains since 2000 (according to Morningstar data).
VTI and VTSAX both distribute dividends, which incur taxes in the year of receipt. The distribution frequency differs: VTI typically distributes quarterly, while VTSAX does so annually. This variance can affect cash flow and tax planning strategies.
In 2022, both funds reported similar dividend yields (approximately 1.8%). The majority of these dividends qualified for taxation at the lower long-term capital gains rate rather than as ordinary income.
VTI’s intraday trading capability offers more flexibility for tax loss harvesting. Investors can respond to market movements in real-time, potentially capturing losses to offset gains elsewhere in their portfolio.
VTSAX, with its end-of-day pricing, provides fewer opportunities for intraday tax loss harvesting. However, long-term investors who prefer a hands-off approach may not find this limitation significant.
Both funds aim for tax efficiency, but their structures create some differences. VTI’s ETF structure allows greater control over taxable events, potentially resulting in fewer surprise tax bills at year-end.
VTSAX has achieved remarkable tax efficiency despite its mutual fund structure. Vanguard’s unique approach to managing this fund has resulted in a tax-cost ratio that competes with many ETFs.
Morningstar data shows that over the past three years, VTI had a tax-cost ratio of 0.60%, while VTSAX’s was slightly lower at 0.46%. This suggests VTSAX may have a slight edge in tax efficiency, contrary to many investors’ expectations.

The choice between VTI and VTSAX often depends on individual investment strategies and personal tax situations. While both funds offer excellent tax efficiency, the best choice hinges on factors such as trading frequency, investment horizon, and overall portfolio composition.
As we move forward, let’s examine the various factors that can influence the tax efficiency of these funds and how they might impact different types of investors.
Trading volume impacts tax efficiency significantly. VTI, an ETF, has higher daily trading volumes. This liquidity benefits tax-loss harvesting, allowing investors to sell shares quickly to offset capital gains in their portfolio. ETFs can be more tax efficient compared to traditional mutual funds. Generally, holding an ETF in a taxable account will generate less tax liabilities.
VTSAX, a mutual fund, typically has lower trading volumes. This can result in fewer taxable events, which benefits long-term, buy-and-hold investors. Vanguard’s unique structure for VTSAX has narrowed the tax efficiency gap between the two funds considerably. The 2023 expiration of a Vanguard patent and exclusion of ETF share classes from Rule 6C-11 led to a surge in SEC exemptive relief filings.
Expense ratios directly affect returns and tax efficiency. VTI’s lower expense ratio (0.03% vs VTSAX’s 0.04%) means investors receive more of the fund’s returns. Over time, this difference can compound, potentially leading to higher taxable distributions for VTI holders.
However, we shouldn’t overstate this small difference. Both funds rank among the most cost-effective in the market. The 0.01% difference will unlikely alter most investors’ tax situations significantly.
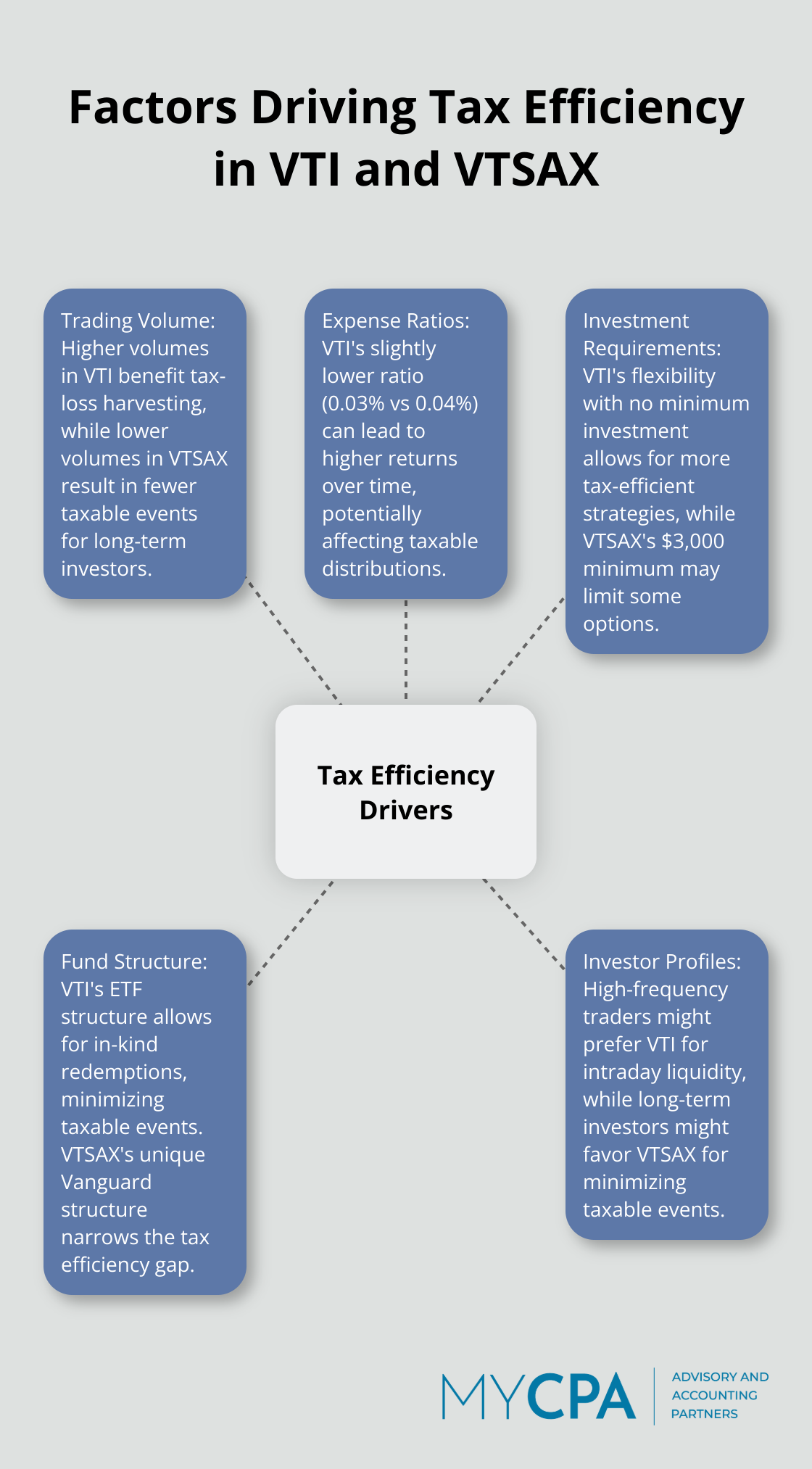
Minimum investment requirements influence an investor’s ability to implement tax-efficient strategies. VTSAX’s $3,000 minimum investment may restrict some investors’ ability to dollar-cost average or rebalance their portfolio tax-efficiently.
VTI offers more flexibility with no minimum beyond the price of a single share. This benefits investors who want to make small, regular investments or fine-tune their portfolio allocation without triggering significant taxable events.
The choice between VTI and VTSAX often depends on individual circumstances. High-frequency traders might prefer VTI for its intraday liquidity. Long-term investors might favor VTSAX for its potential to minimize taxable events.
Investor profiles and goals play a key role in determining the most tax-efficient option. Retirees drawing regular income might benefit from VTI’s flexibility. Young professionals automatically investing each paycheck might find VTSAX more convenient.
These factors don’t operate in isolation. The interplay between an investor’s overall financial situation, investment strategy, and these fund characteristics determines the most tax-efficient choice. Investors should consider their unique circumstances when deciding between VTI and VTSAX.
The VTI vs VTSAX tax efficiency debate lacks a clear winner. Both funds offer excellent tax efficiency due to Vanguard’s innovative management approach. VTI’s ETF structure provides flexibility for tax-loss harvesting and intraday trading, which active investors might prefer. VTSAX, despite its mutual fund structure, achieves remarkable tax efficiency, often matching or surpassing VTI in certain years.
Your individual circumstances determine which fund proves more tax-efficient for you. Consider your investment goals, trading frequency, and overall financial strategy when making your choice. Other factors, such as expense ratios, minimum investment requirements, and personal preferences, should also influence your decision.
Tax laws and individual financial situations involve complexities. We at My CPA Advisory and Accounting Partners recommend consulting with a tax professional before making significant investment decisions. Our team of experts can provide personalized advice tailored to your unique circumstances. For comprehensive tax and financial planning services, visit our website to learn how we can help you optimize your investment strategy.








Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions | Powered by Cajabra